Liver Cancer Treatment in Mumbai
Types of Liver Cancer: Primary and Secondary Liver Cancer
Liver cancer can be primary or secondary. Cancers that begin in the liver are called primary liver cancer. Cancers that arise in the other parts of the body and spread to the liver are called secondary liver cancer or metastasis. Primary liver cancer includes
- Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (arising from the bile duct inside the liver )
Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) tends to occur in livers damaged by alcohol abuse, or chronic infection with diseases such as hepatitis B and C or rare birth defects. More than half of all people diagnosed with primary liver cancer have cirrhosis.
Secondary Liver Cancer and Liver Metastasis from Colon, Stomach & Pancreatic Cancers
The male-to-female ratio for HCC in India is 4:1. The age of presentation varies from 40 to 70 years.
Secondary liver cancer or metastasis liver is the most common cancerous condition of liver. It depends on the location of the original cancer. Primary cancers that are most likely to spread to the liver are cancers of the:
- Colon
- Rectum
- Stomach
- Esophagus/ Stomach Pancreas
Even if the primary cancer is removed, liver metastasis can still occur years later. If you’ve had cancer, it’s important to learn the signs of liver metastasis and get regular checkups.
Early Signs & Liver Cancer Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
- Jaundice – yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes
- Abdominal pain – often on the right upper abdomen
- Loss of weight and appetite
- Hepatomegaly – enlarged liver, the abdomen may appear swollen
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Back pain
- General itching
- Fever
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer: Tests, Scans and Biopsy
- Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your abdomen to look for any in the upper abdomen. He also examines your eyes and skin to look for evidence of jaundice
- Blood tests: complete blood count, LFT, RFT, Serum electrolytes, coagulation profile, HIV, HCV &HBV testing, tumor markers like AFP, CEA, Ca19-9.
- Radiological imaging USG Abdomen, Triple phase CT Scan of the abdomen, MRI Abdomen, CT Angiography, PET Scan as required
- Biopsy: Liver biopsy is sometimes required but not always. Your cancer surgeon will be the best person to decide if it is needed.
Advanced Liver Cancer Treatment Options at Specialist Hospitals in Mumbai
There are various modalities of treatment for HCC and IHC.
Surgery
A surgical resection is the best curative option for primary liver cancer. It involves the removal of the tumor with an adequate margin of normal liver. At times when the underlying liver is too unhealthy, a resection may not be possible. Liver transplantation is an option in select cases.
Liver Directed Therapy
When the tumors are not amenable for surgery or ablation , liver directed therapies like Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) are performed. These are performed by the interventional radiology team.. Treatment options depend on the stage of the disease, General condition of the patient and associated comorbidities.
Ablation
Loco-regional ablative techniques like Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or Microwave ablation (MWA) can be used in smaller tumors with good results. We perform this routinely with our interventional radiology team.
Medical Management
If the tumors are multiple or patients are not eligible for any of these treatments, we refer them to the medical oncologists for certain oral immunotherapy or targeted therapy agents which may halt the rate of spread of these tumors.
Treatment of Liver
Metastasis from Colorectal &
Neuroendocrine Cancers
Treatment of metastasis in the liver
The liver is the most commonly involved organ in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer.
Colorectal and neuroendocrine are the cancers where it is
worthwhile aggressively treating this liver metastasis since
many patients do well.
Advanced Treatment Options for Liver Metastasis
-
Surgery
Aggressive surgery to resect this liver metastasis is the best way to cure these patients. Patients with solitary metastasis have a more than 60% 5-year survival. At times, we give chemotherapy to downsize the lesions before embarking on surgery.
-
Ablative techniques for liver metastasis
Radiofrequency ablation(RFA) and Microwave ablation (MWA) for liver metastasis can be used in cases where surgery is not possible of the lesions are too deep-seated.
-
Chemotherapy
Radiofrequency ablation(RFA) and Microwave ablation (MWA) for liver metastasis can be used in cases where surgery is not possible of the lesions are too deep-seated.
-
Surgery For Liver Cancers
There are various types of resections for liver tumors.
- Right or Left hepatectomy- involves removal of the right or left half of the liver. These are major surgeries that need a proper preoperative planning.
- Extended right/ left hepatectomy- involves removal of more than 60-70 % of the liver. Needs a volumetric assessment to preserve enough liver tissue.. these are the most complex liver surgeries
- Segmental resection- removal of only one or two segments.
- Nonanatomical resection- usually for liver metastasis.
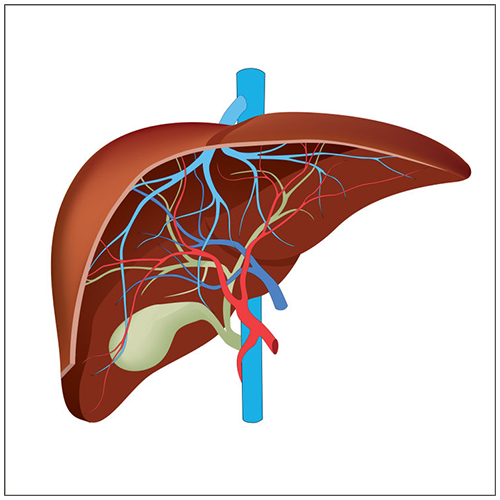
This illustration shows the liver and its blood supply.
It highlights the hepatic artery (red), portal vein (blue), and bile ducts (green)—structures that are crucial in understanding liver tumors, blood flow, and how treatments like surgery, ablation, or liver-directed therapies are planned.

Have Questions? Connect with Us
Related FAQ’s
1. How can gastric cancer be diagnosed early?
Gastric cancer is indolent cancer with vague symptoms and hence many patients present late. Any loss of weight with loss of appetite, persistent indigestion or gastric bloating, or vomiting must be promptly investigated.
2. Can I function normally if my stomach is removed?
Yes. Most patient’s liver is near-normal lives after a gastrectomy. Some alterations in lifestyle like the inability to take in a large meal at one time will need some coping. Small frequent meals are advised.
3. I have been diagnosed with gastric cancer? Is there a risk of transmission to my family members?
Not at all. No cancer is transmitted from one person to another. Patients need all the love and care they can get from their family members and friends in order to fight this disease.
4. What are my survival chances after surgery for gastric cancer?
Survival after gastric cancer depends on the stage of the disease as per the histopathology report. Node-negative patients do better than node-positive ones. Early gastric cancer has a survival of more than 65% at 5 years with complete and appropriate radical surgery while locally advanced gastric cancers have a 25% 5-year survival in spite of multimodality treatment.
5. How often should I follow up after my treatment is completed?
You must follow up at 6 monthly intervals up to 5 years after completing treatment for gastric cancer. The usual tests area CBC, B12 levels, chest Xray and ultrasonography or CT scan of the abdomen.
Related Blogs
Feeding Tube in Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, is a significant health concern globally, with a rising incidence in India. According to the National Cancer...
Why are my Stools Black ? Key reasons and what to do?
If you’ve recently noticed that your stools have turned black, it’s natural to wonder if it’s a cause for concern. In India, where digestive…
Causes and Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is one of the fastest-growing cancers worldwide, with a high prevalence in countries like India due to risk factors such as hepatitis...